It will definitely be part of the application process along with proof of employment. Knowing where you stand ahead of time will prevent surprises at the bank. Doing your own inventory may also prompt you to prepare your finances before going to the bank. If nothing else, it will prepare you for the in-depth process of applying for a mortgage. The opposite of an asset, a liability is anything you are responsible for financially or anything you do not own outright.
- You’ll list all the assets on the left side and your liabilities on the right.
- Our goal is to give you the best advice to help you make smart personal finance decisions.
- If you’re using the wrong credit or debit card, it could be costing you serious money.
- When it comes to your credit and your potential to borrow money, it is important to have a good understanding of both assets and liabilities.
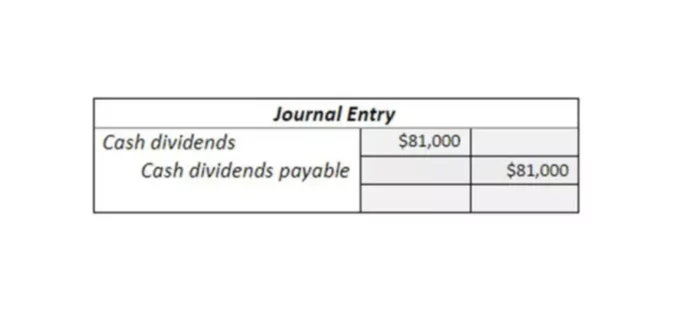
- For example, the bank sold $75,000 worth of its shares to the public as stock, which becomes the liability, which the bank owes to the public.
Lenders will want to have a detailed look at both before entering into any agreement. These are financial institutions willing to lend large sums over 30 years so they will want to know as much about your current financial picture as possible. On the flip side, if you have more liabilities than assets, this will have a negative impact on your credit and your ability to obtain a mortgage. So as you can see, having a good balance of assets and liabilities, and knowing where you stand currently will help you overall as you apply for mortgages. The balance sheet always balances because of the double-entry method of accounting practiced, and assets always equal liabilities plus net worth.
Alert: highest cash back card we’ve seen now has 0% intro APR until 2024
We’re transparent about how we are able to bring quality content, competitive rates, and useful tools to you by explaining how we make money. Assets help you run your business smoothly, even when your earnings aren’t as high as expected. They give you confidence you can expand your business and set ambitious financial goals. Put simply, you need to evaluate whether leasing or buying a car will put you in a better financial position.

It can be real (e.g. a bill that needs to be paid) or potential (e.g. a possible lawsuit). For example, if a company has more expenses than revenues for the past three years, it may signal weak financial stability because it has been losing money for those years. Liability may also refer to the legal liability of a business or individual. For example, many businesses take out liability insurance in case a customer or employee sues them for negligence.
Our editors and reporters thoroughly fact-check editorial content to ensure the information you’re reading is accurate. We maintain a firewall between our advertisers and our editorial team. Our editorial team does not receive direct compensation from our advertisers.
What Is a Liability?
A liability is something a person or company owes, usually a sum of money. Liabilities are settled over time through the transfer of economic benefits including money, goods, or services. You buy inventory on account, so your inventory balance goes up, but you need to pay the invoice, so your liabilities go up as well. If you were to stick to accounting only, every business would be worth just the value of its assets minus all liabilities.

The current/short-term liabilities are separated from long-term/non-current liabilities on the balance sheet. All accounting statements can be traced back to individual transactions, and every transaction has to balance. Liabilities are other people’s claims on your assets, and equity in accounting is your claims on your assets.
Cash in hand, reserves, and property owned are major assets, and outstanding stock and checkable deposits are major claims on a commercial bank’s balance sheet. Current assets can be converted into cash quickly, typically under one year. Another common term for current assets is short-term investments. You must pay short-term liabilities within one year of incurring the debt. Long-term liabilities include debts you pay over a period that is longer than a year. As a practical example of understanding a firm’s liabilities, let’s look at a historical example using AT&T’s (T) 2020 balance sheet.
Assets vs. liabilities: What’s the difference?
Expenses can be paid immediately with cash, or the payment could be delayed which would create a liability. Assets are resources the business owns, such as cash, accounts receivable, and equipment. Liabilities are obligations the company has—in other words, what the company owes to others, such as accounts payable and long-term debt. Usually, a company’s balance sheet is divided into two columns. You’ll list all the assets on the left side and your liabilities on the right.
It’s important to recognize these liabilities and try to find ways to minimize them. For example, Hourly connects workers’ comp directly with payroll–so premiums are always accurate and you’re never paying for more or less coverage than you actually need. Together, assets and liabilities make up your overall financial picture, and will be carefully looked at when you apply for new credit.
- Instead, a leased vehicle is a liability for the business even though the business has temporary possession of the car.
- Normal terms will give you the opportunity to pay in 30 days.
- Like liabilities, businesses can have current and fixed assets (aka noncurrent assets).
Again, long-term liabilities are typically not due for settlement within the same year. While they aren’t urgent, keeping track of your long-term liabilities will save you from unpleasant financial surprises. Keep an eye on your short-term liabilities as they have the potential to disrupt your daily operations. For example, say you need to buy $1,000 worth of raw materials this week. You’d need to ensure you have $1,000 ready to pay the supplier so production doesn’t stop.
What is a business debt schedule?
We do not include the universe of companies or financial offers that may be available to you. Below are examples of a few types of small businesses and the assets and liabilities they may have. The inventory you receive is an asset that will help you make money from the new projects. But the amount you need to pay back to suppliers is a short-term liability. The flip side is that you’ve taken out a mortgage, and that’s a long-term liability. You’ll need to make extra money to pay off this long-term debt.
He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem. The Ascent is a Motley Fool service that rates and reviews essential products for your everyday money matters. It might be tricky to attach dollar amounts to certain things. For example, if your company has a sizable social media following, you might use this calculator to arrive at a number to attribute to your asset. Let’s look at each individually to help you get a better feel for how all of this should break down at your company. Remember, accounting is all about balance — they call it “balancing your books” for a reason.
So if you have more assets than liabilities your ability to pay your mortgage will look more favorable. Put plainly if you own more than you owe, you will be in good shape for a mortgage or other loan. Like liabilities, businesses can have current and fixed assets (aka noncurrent assets). A current asset is a short-term asset, while noncurrent assets are long-term. An expense is the cost of operations that a company incurs to generate revenue. Unlike assets and liabilities, expenses are related to revenue, and both are listed on a company’s income statement.
How Do You Calculate Assets and Liabilities?
Instead, an annual depreciation charge is taken from the asset so that the expenses match the timing of the income statement. If you use a building for 20 years, you don’t want to expense it all at once. For an individual, the primary asset may be his or her house. The difference between the house asset and the mortgage is the equity of the owner in the house. We are an independent, advertising-supported comparison service. Owners’ or shareholders’ equity also appears on the balance sheet, just beneath liabilities.
But you can’t necessarily sell that brand recognition on its own. Your inventory, on the other hand, is an asset you can sell. But sometimes assets and liabilities aren’t that easy to identify. All information contained herein is for informational purposes only and, while every effort has been made to ensure accuracy, no guarantee is expressed or implied.
Since most companies do not pay for goods and services as they are acquired, AP is equivalent to a stack of bills waiting to be paid. For most small businesses, the only long-term liabilities will be term loans from banks. This would include everything from a three-year loan for a trailer to a 20-year loan for a building. When you sell something on account, you create an accounts receivable (AR) that is an asset on your balance sheet.
We should start by talking about the accounting equation. This equation was drilled into my head for a couple of years when I started my accounting major. Then, when I was a teaching assistant, I drilled it into many other students’ heads. Our experts have been helping you master your money for over four decades.
If you do the math before, you will have a better handle on your chances of obtaining a mortgage and save time during the application process. Both assets and liabilities are on the balance sheet, which is one of the three main financial statements for businesses. Generally, liability refers to the state of being responsible for something, and this term can refer to any money or service owed to another party. Tax liability, for example, can refer to the property taxes that a homeowner owes to the municipal government or the income tax he owes to the federal government. When a retailer collects sales tax from a customer, they have a sales tax liability on their books until they remit those funds to the county/city/state. This usually differs slightly from the market value of the company.
